The world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is full of terms like Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI), Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Deep Learning (DL). For those new to AI, these concepts can seem daunting and confusing. But don’t be discouraged—understanding the differences between these terms is the key to unlocking the potential applications and limitations of AI technologies.
In this article, we’ll examine these key terms, breaking them down with easy-to-digest examples so you can cover the basics and better understand the world of AI.
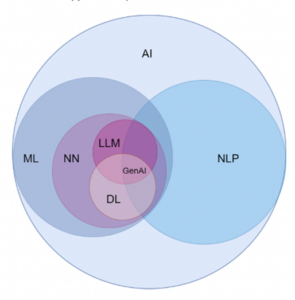
Figure 1. Key Concepts of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (Mishra, 2023).
Generative AI (GenAI): The AI Artist
Imagine a system that can write stories, compose music, or even create realistic images and videos. That’s GenAI. It learns patterns from existing content and uses them to generate new, quasi original creations.
Think of it like a chef who learns from various recipes and then creates unique dishes. GenAI tools like ChatGPT and DALL-E are examples of this technology in action, showing impressive creative potential. However, it’s important to remember that GenAI is not truly “creative” as it relies on existing data and patterns. Anything not within its training data cannot be considered for a generative output, and so cannot be present within anything it creates.
The most common example of GenAI is OpenAI’s ChatGPT, which can write human-like text in a fraction of the time it would take humans, or OpenAI’s DALL-E, which generates original images from text descriptions, albeit with notable safeguards in place. OpenAI also recently introduced a video generation product named Sora, which can generate photo real video clips.
While we’re still in the early days of what this technology will ultimately be able to do, GenAI has already made an immense impact across many fields, from creative industries to education, marketing, applied science, medical research, and even information technology (IT).
Machine Learning (ML): Learning from Experience
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of artificial intelligence that teaches computers to understand data and perform tasks by learning from experience without explicit programming. Generative AI is a branch of AI that uses machine learning to create new content that resembles training data. Just like we as humans learn from experience, ML algorithms allow computers to analyze data and make predictions or decisions. This technology powers various applications, from spam filters to stock market prediction tools.
For instance, a grocery store could use ML to analyze past sales data and predict future demand, optimizing their inventory and mitigating waste.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Bridging the Communication Gap
Natural Language Processing (NLP) focuses on enabling computers to understand and generate human language. It combines AI with linguistics to make interactions between humans and computers more natural.
A key development in NLP is the Transformer model, which allows AI systems to understand the context and meaning of words in a sentence, rather than just processing them sequentially. This has led to the development of Large Language Models (LLMs), like the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), which can generate human-like text with a high degree of coherence and relevance.
NLP is the technology that allows us to use voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, or to get relevant search results even when our queries are not precise.
Natural Language Processing is a vital building block that has enabled many revolutionary advancements in GenAI that have been made available to the public. It’s through these ways of breaking apart a sentence and analyzing it for meaning, that an AI system can begin to understand what a person is requesting from it. This applies not only to entered text, but to spoken text as well, regardless of what language you speak.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning: Mimicking the Brain
Neural Networks are AI systems inspired by the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes that process information and recognize patterns. Deep Learning (DL) is a type of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze complex data such as images and speech.
These technologies are the driving force behind many AI applications, including facial recognition and self-driving cars.
Learn more about the most popular neural networks.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): The Ultimate Form of AI?
While the technologies mentioned above are examples of “narrow AI” designed for specific tasks, AGI refers to a theoretical type of AI that can learn, understand, and think for itself like a human. This is probably the version of AI you often hear people talk about when they mention AI surpassing human capabilities. But don’t fear, this ultimate form of AI is more science fiction than reality.
While AGI is still fictional, it sparks many exciting possibilities and ethical debates for the future.
Understanding AI for a Better Future
Understanding the different types of AI and their capabilities is crucial in today’s world. Whether you’re a business owner, a creative professional, or simply curious about technology, this knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions and leverage the potential of AI.
As AI continues to evolve, it’s essential to stay informed and participate in shaping its development for the benefit of humanity. Having a clear grasp of these concepts will help you get the most out of this emerging technology as you apply it in your personal and professional life.
